soil water permeability test|soil permeability test procedure : wholesaling General. Most rock and soil contains numerous open spaces where water may be stored and through which water can move. Permeability, or hydraulic conductivity, is a measure of the . webMr Jack Vegas Sister Sites are getting all the hype for the features like 100% Bonus, 50 Free Spins and NetEnt Slots for the players. No Deposit Free Spins on Registration
{plog:ftitle_list}
Descubra os 20 filmes similares ao filme O Gângster dirigido .
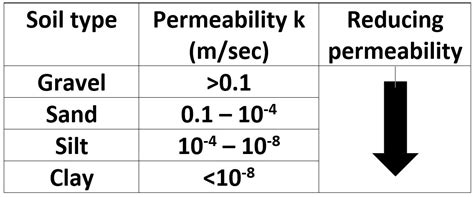
typical permeability values of soil
8 Permeability Test. Introduction. Soil permeability (hydraulic conductivity) is the rate at which water flows through soil materials. It is an essential characteristic across a broad spectrum of engineering and earth-science disciplines. See moreSoil permeability can be estimated using empirical methods like soil survey mapping, soil texture, or particle size distribution. However, a variety of different laboratory and field test methods make it just as easy to measure these .General. Most rock and soil contains numerous open spaces where water may be stored and through which water can move. Permeability, or hydraulic conductivity, is a measure of the . Soil permeability is a measurement dictating how quickly water can pass through a soil sample. We use permeability testing to assess how effectively soil allows water to travel through it. In general, water travels .
Soil permeability governs how water flows through the ground, affecting the performance of buildings, roads, and even earthen dams. In this blog post, we delve into the fascinating world of soil permeability, its importance in . The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. Soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when .Standardized soil permeability tests help assess site drainage capacities and seepage losses for various geotechnical applications. This overview covers common soil permeability test methods, result interpretations, and key .
The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. Soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when . Soil permeability test tells how quickly water moves through the soil, helping you design stable and sustainable projects. Read more!Apparatus for Constant Head Permeability Test. Permeameter mould, internal diameter = 100mm, effective height =127.3 mm, capacity = 1000ml. . Take a small specimen of the soil in a container for the water content determination. . What is Soil Permeability? Soil permeability is a measurement dictating how quickly water can pass through a soil sample. We use permeability testing to assess how effectively soil allows water to travel .
Interpreting Test Results. Analyzing the results from these tests can reveal much about your soil’s health and water management needs. High permeability indicates quick drainage, which can be ideal for certain plants .The coefficient of permeability varies with the void ratio as e/sup>/(1+e). For a given soil, the greater the void ratio, the higher the value of the coefficient of permeability. Here 'e' is the void ratio. Based on other concepts it has been established that the permeability of a soil varies as e 2 or e 3 /(1+e). Whatever may be the exact .Infiltration and percolation are two concepts that describe the rate at which water moves into the soil (infiltration) and through the soil profile, vertically and horizontally (percolation). And permeability explains how well water can move through the porous media or the soil. Water movement in soil video:
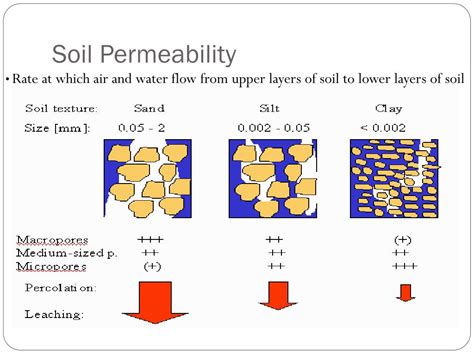
Infiltration and permeability describe the manner by which water moves into and through soil. Water held in a soil is described by the term water content. Water content can be quantified on both a gravimetric (g water/g soil) and volumetric (ml water/ml soil) basis. The volumetric expression of water content is used most often. Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. 9.8: Soil Permeability - Geosciences LibreTexts
FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined
The discharge (apparent) seepage velocity of water based on the gross cross-sectional area of the soil, or A q v However, water cannot be flowing through solid particles but only through the voids or pores between the grains. The average velocity at which the water flows through the soil pores is obtained by: A v q v s v s is called the SEEPAGE .
This video explains the procedure of constant head test to determine the soil permeability. This test is performed on coarse-grained soil with a high coeffic.
If the depth of penetration of water is less than or equal to 25mm, the specimen passes the permeability test. If the depth of penetration of water is more than 25mm, the specimen is considered to have failed the permeability test. Record the test results in a tabular form, indicating the depth of penetration of water for each specimen and the . Procedure for the Falling Head Soil Permeability Test. The falling head soil permeability test works like the constant head test. The difference is that the water head will not be constant but will decrease/fall with time. The step-by-step procedures for the falling head permeability test are as follows:The SI unit for permeability is the square metre (m 2).A practical unit for permeability is the darcy (d), or more commonly the millidarcy (md) (1 d ≈ 10 −12 m 2). The name honors the French Engineer Henry Darcy who first described the flow of water through sand filters for potable water supply. Permeability values for most materials commonly range typically from a fraction to . The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 – Part 36, 1975).
When you take an undisturbed sample to a testing laboratory, to measure permeability, a column of soil is placed under specific conditions such as water saturation and constant head of water. The result will be given to you either .
typical permeability of soils
The Chemistry of Saline and Sodic Soils. Donald L. Sparks, in Environmental Soil Chemistry (Second Edition), 2003 Drainage. Poor drainage can also cause salinity and may be due to a high water table or to low soil permeability caused by sodicity (high sodium content) of water. Soil permeability is “the ease with which gases, liquids or plant roots penetrate or pass through a .Permeability. Permeability is a physical property of a porous material that permits the flow or passage of water under saturated or nearly saturated conditions through interconnected voids in soil in which flow may be in the form of laminar flow or turbulent flow, practically flow problems of water in soil mechanics through its interconnecting voids ,in most of case flow is laminar, the .
Permeability of soil- water strongly affects the engineering properties for most kind of soils and water is an important factor in most geotechnical problem. . Temperature during testing is 27°C. Flow through soil is laminar; Entire cross sectional area is available for flow;The permeability coefficient can be calculated when the water in the standpipe has reached a previously determined level. The calculation takes into account the size of the sample, the cross-sectional area of the standpipe, as well as the time it took to change the water level. Soil Permeability Testing Equipment: Permeability Cells (Flexible . The soil water characteristic curve can be used to indirectly determine the soil shear strength, permeability, change in water volume, water holding capacity and water availability. Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the test which basically works the same as the constant head permeability test, the only difference being that the water head will not be constant but diminishing over time. This test .
The permeability test is the measure of the flow of a liquid through a soil sample. Permeability testing can be done using 3 different procedures. . while the water is allowed to flow through the soil sample and the outflow is collected. This is measured at regular time intervals. Falling Head Permeability Test. This is also known as the Variable head permeability test. The head-causing flow in this method is not as constant as in the previous method. The falling head permeability test is employed for the permeability of soil like fine-grained soil, and clay. Fig.2. Falling Head Permeameter While most soil experts believe that soil observation can provide enough information to design an effective septic system, most states today also require perc testing to directly measure the rate at which water percolates through the soil. The test measures how fast water drains into a standard-sized hole in the ground.
The findings indicate that the triaxial test demonstrates the highest permeability, whereas the falling head test exhibits the lowest. . Determination of permeability of a soil-Constant head method using a flexible wall permeameter. Google Scholar. . Application of an Unknown Substance to Imitate Water Damage. Next. Open in viewer. Go to .PERMEABILITY TEST 1. Objective The rate of flow of water, under laminar flow conditions, through a unit cross sectional are of soil mass, under unit hydraulic gradient, is defined as coefficient of permeability. Permeability of the soil governs the magnitude of excess pore water pressure built-up The presence of water affects the properties of the soil it encounters. The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. Soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when under a unit hydraulic gradient.

how to test arm torsion strength
webLista de jogos e resultados oficiais da UEFA Champions League 2023/2024. O UEFA.com funciona melhor noutros browsers. Para a melhor experiência possível recomendamos a utilização do Chrome, Firefox ou Microsoft Edge. Saltar para o conteúdo principal. Sobre a UEFA ; UEFA.tv
soil water permeability test|soil permeability test procedure